Cryptocurrency wallets occupy a very important place in the world of digital assets. They are the primary tool for storing and managing coins. Compared to the traditional financial system, such a wallet is simultaneously a bank card, an online bank, and a safe for your funds. Without it, you cannot fully use cryptocurrency: send, receive, and store it.
For many newcomers, the term "wallet" sounds misleading. It may seem like it's just an app where assets are stored. In reality, it's not quite that simple.
Crypto wallet — is a digital tool for storing and managing cryptocurrencies. It is not a physical storage, as it may seem at first glance. In fact, the user's funds are always on the blockchain — a decentralized database. A crypto wallet gives you access to them using special keys.
To understand how it works, imagine the blockchain as a public ledger where all transactions are recorded. Your wallet does not "store" coins; it shows you the page of that ledger that states you are the owner of a certain amount of cryptocurrency.
Watch our detailed video about crypto wallets to get all the details:
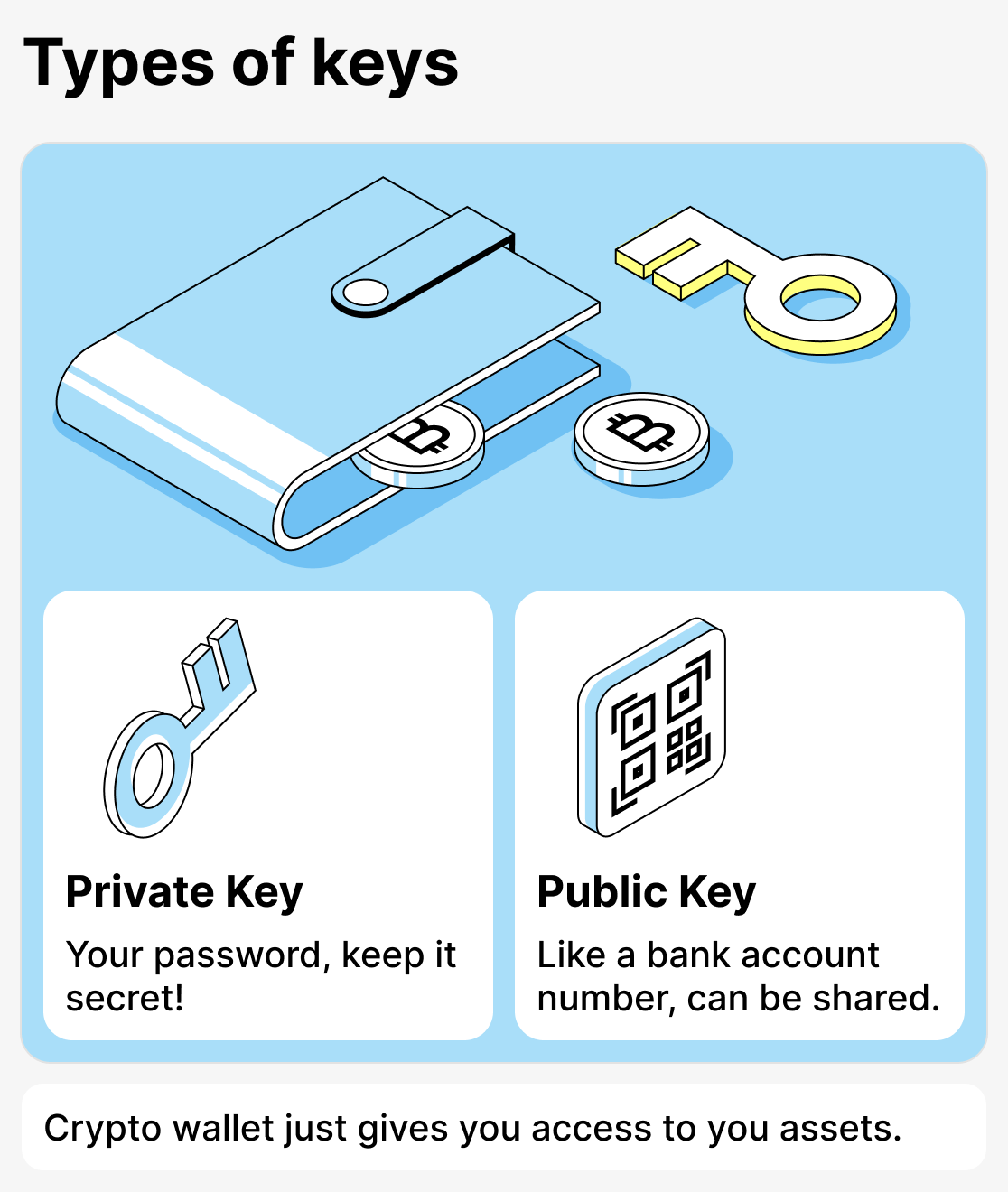
Public and private keys: what's the difference
Any wallet has two keys:
- Public key (address) — is the number of your crypto wallet. It functions like a bank account number. It can be freely shared with others so they can transfer funds to you. It usually appears as a long string of letters and numbers. Such a key is often presented as a QR code.
- Private key — your personal password or digital signature. With it, you confirm transactions and get full access to your funds. This key must never be shown to anyone! If someone learns your private key, they can withdraw all funds without your consent.
- Often, together with the private key, the user is prompted to create a special seed phrase. It is a set of 12-24 random words. The seed phrase is a kind of "master key": if you lose your phone or another device with the blockchain wallet installed, you can easily restore access with it.
Thus, a crypto wallet is not a device or an application where money is stored, but a specialized tool that verifies your ownership of cryptocurrency on the blockchain and allows you to manage your assets.
Types of crypto wallets
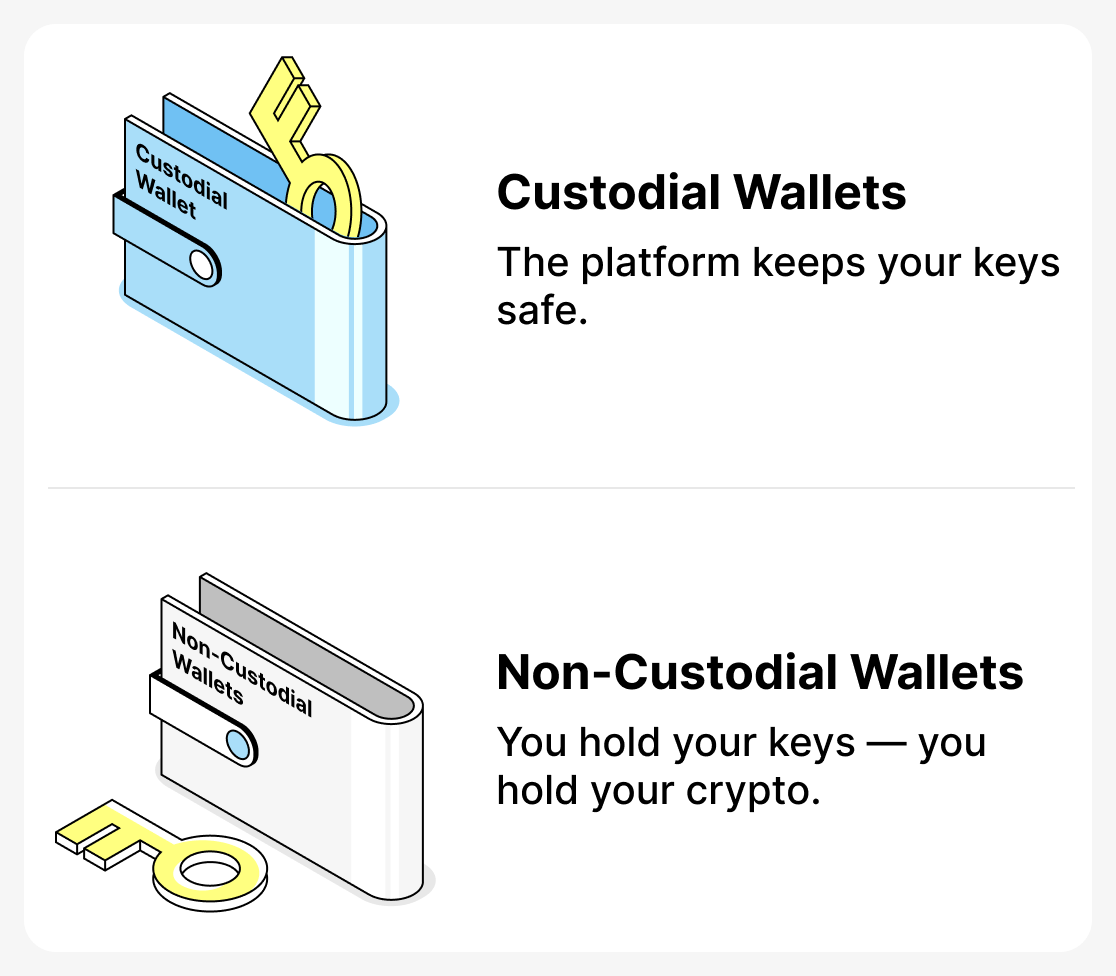
Crypto wallets come in different types. Which one to choose depends on how you plan to use cryptocurrency. Crypto wallets are divided into two main groups: Custodial and Non-custodial.
Custodial wallets
Custodial wallets — are services where private keys are stored by the platform and assets are managed through it. The user entrusts the organization with security and management, while complex technical processes are handled by professionals.
With a custodial wallet, you don't need to worry about keeping your private keys or seed phrase safe. Transactions are carried out in a simple, user-friendly app, making it much easier to work with cryptocurrency.
And here's what that means: no mistakes with private keys, no risk of accidentally losing access. At the same time, all asset management features are available to the user!
Features of custodial wallets
- Simplicity and ease of use – the user works only with the interface. All technical matters are handled by professionals. Even a beginner can easily figure out transfers, purchases, and asset management.
- Professional asset protection – private keys are held by the service, reducing the risk of hacking or loss of funds.
- User support – custodial wallets help and support customers so they can quickly resolve any issues and navigate the service.
- Security without unnecessary complexity – the user does not need to remember or write down private keys; the service ensures their safekeeping and manages the keys itself.
Custodial wallets allow a user to focus on managing assets and increasing their returns. These are services where the platform takes care of everything. It's like VIP service at a bank: clients entrust asset management to specialists who ensure everything runs smoothly. There is support, the user is always protected from making mistakes, and their funds are insured. It's simple — you are the client, and professionals handle security.
Non-custodial wallets
Non-custodial wallets — are wallets where the user controls their own assets. Unlike custodial wallets, the private keys are not stored by the service, but are held by the clients. You manage your cryptocurrency directly, and the service or platform provides an interface for interacting with the network.
You are solely responsible for the safekeeping of your assets and seed phrase. Yes, you fully control your assets when using a non-custodial wallet, but this places certain responsibilities on you: if you lose your seed phrase, it will be impossible to restore access to your funds.
Features of non-custodial wallets
- The user is solely responsible for safeguarding their private keys and seed phrase.
- Suitable for experienced users who are ready to take full responsibility and control their transactions.
- For beginners, non-custodial wallets can be a complex and risky option.
Non-custodial wallets give you full control over your assets, but, as is well known: the more freedom — the higher the risks!
There is a common belief that if private keys are stored only with you, then you own your funds and nothing will happen to them. In practice, however, over the past 10 years most major financial losses have occurred because users lost control of their seed phrase: they forgot it, misplaced it, or had it stolen by malicious actors.
At the same time, custodial wallets have proven their reliability. To manage your funds, you only need to know your email, password, and enable two-factor authentication. There's no need to write down keys on paper, buy engraved metal plates, or hide them in a safe. Custodial wallets significantly simplify working with cryptocurrency and provide a high level of security. Moreover, users still retain control of their assets!
Hot and cold wallets
Custodial and non-custodial wallets are also divided into two groups: hot and cold wallets. Let’s take a closer look at each group.
Hot wallets: fast and convenient
Hot wallets — applications and services that are always connected to the internet. Their key advantage is convenience. You can open the app at any time and make a transfer in a few seconds.
The transaction takes just a few seconds: simply enter the recipient’s address or scan a QR code. This will be especially useful for those who actively use cryptocurrency—paying for goods and services, trading on exchanges, or testing new tokens.
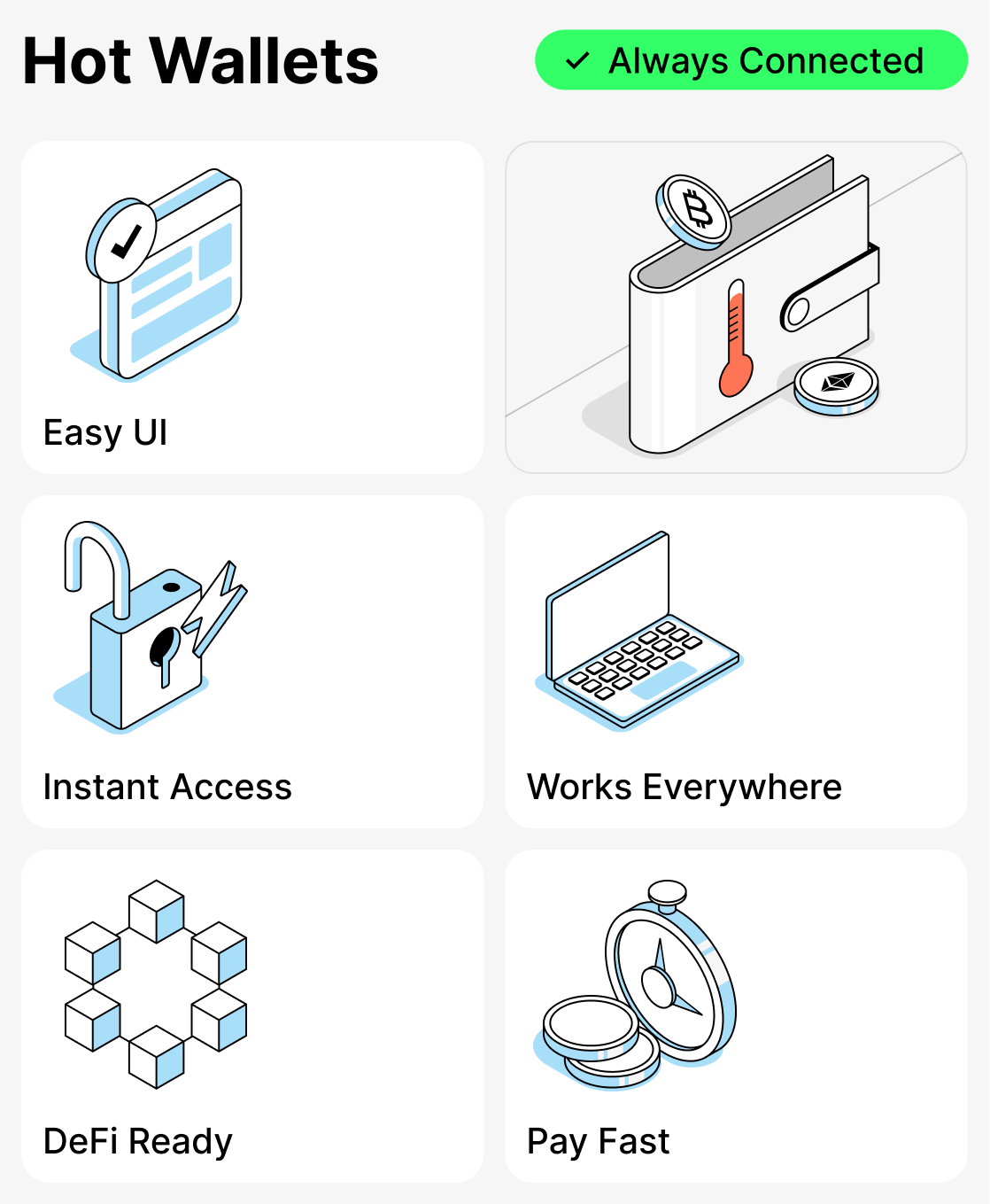
Features of hot crypto wallets:
- Intuitive interface — even newcomers can easily understand and manage their funds;
- Instant access to funds — send and receive cryptocurrency at any time, without delays;
- Integration with exchanges and DeFi — connecting to NFT marketplaces, crypto exchanges, and DeFi protocols makes working with assets convenient;
- Mobility and access from any device — manage cryptocurrency from your smartphone, tablet, or in a web browser;
- Support for payments and purchases — easily pay for goods and services with cryptocurrency without unnecessary conversion.
Hot wallets are really great for everyday tasks. They let you easily pay for purchases, quickly transfer money to other people, or sometimes even buy cryptocurrency. A hot wallet is like your regular wallet or bank card: you always have a small amount of funds on hand that you can use at any moment.
Cold wallets: security above all
Cold wallets — these are specialized physical devices (data carriers), on which private keys are stored. Unlike hot wallets, they are not constantly connected to the internet and are activated only at the moment you decide to make a transaction. This makes them one of the most secure ways to store cryptocurrency.
The most common type of cold wallet is a hardware device. In appearance, they resemble a USB flash drive or a small gadget with a screen and buttons. The wallet connects to a computer or smartphone only when a transaction is being made. The entire confirmation process takes place inside the device, so the private key never leaves it and is never transmitted over the network.
Another option for cold crypto wallets is paper wallets. It's simply a sheet of paper with your private and public keys printed on it, along with QR codes. This method of storing private keys has both advantages and disadvantages. On the one hand, a paper wallet cannot be hacked remotely because it is not physically connected to the internet. On the other hand, paper can be easily lost or damaged, and if it is lost or destroyed, recovering access to your assets will be impossible.
Also, special metal cards and plates, on which the seed phrase is engraved, are sometimes used to store access keys. Their advantage is that they are more durable than paper and can withstand exposure to moisture and fire.
Overall, cold wallets function as a 'digital vault'. They are rarely used for everyday transactions, but are often used to store large amounts for the long term.

Features of cold wallets
- Maximum protection of funds — virtually impossible to steal funds remotely.
- Inconvenience in everyday use — each transaction requires connecting the device, which takes time and needs additional equipment.
- Cost of the device — high-quality hardware wallets usually cost from $70 and up.
- Risk of losing access — if you lose your device or seed phrase, restoring the wallet will be extremely difficult or impossible.
Cold crypto wallets do indeed protect funds well, but using them is often associated with certain difficulties. Moreover, good models are quite expensive, and losing the device or the seed phrase can make it impossible to recover access to the funds.
How a crypto wallet works
Custodial and non-custodial wallets operate somewhat differently. Primarily, they differ in their approach to privacy and access keys:
How non-custodial wallets work
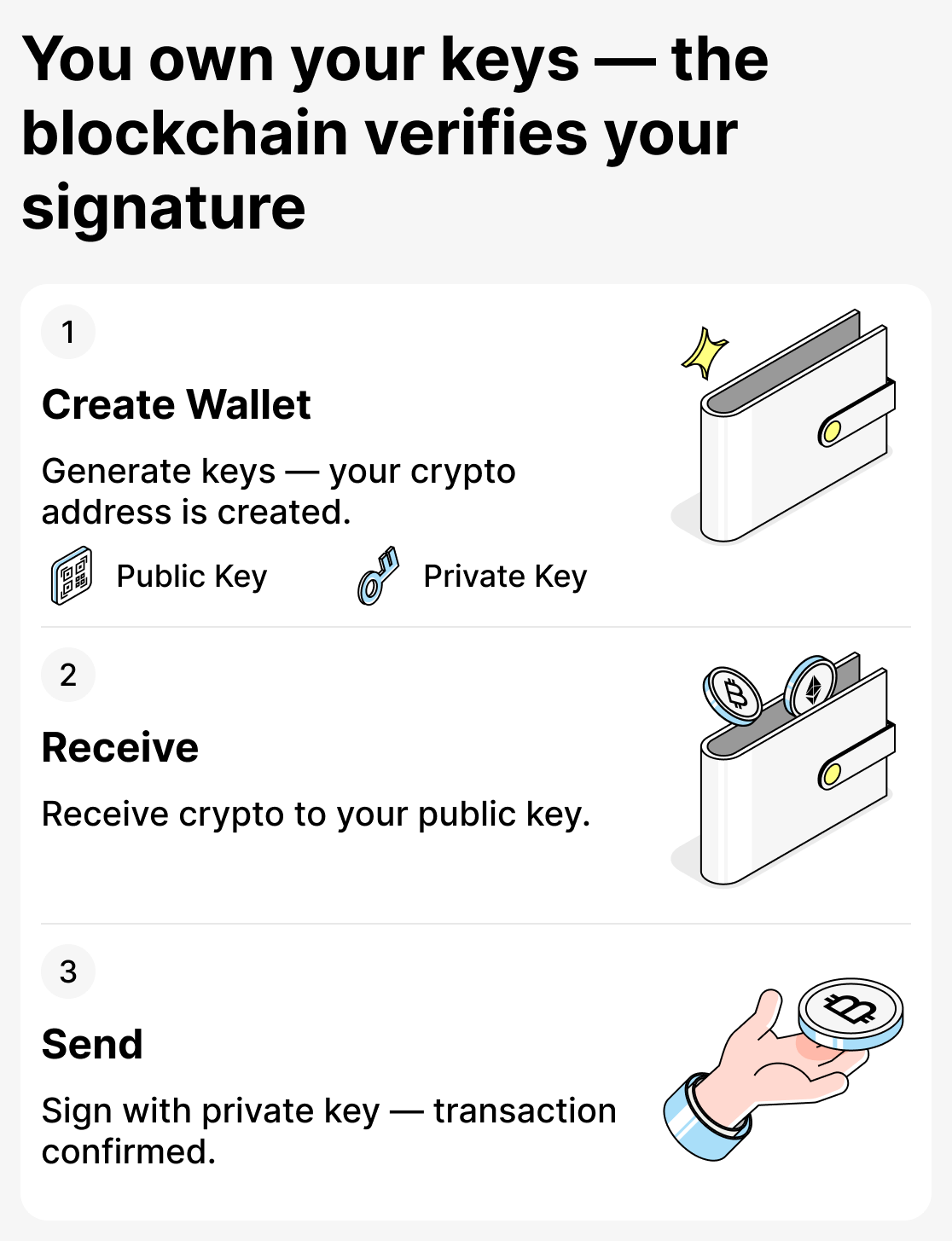
The principle of operation can be described as follows:
- Creating a wallet. The user generates a pair of keys: public and private. Together they form an address linked to the blockchain.
- Receiving funds. The sender specifies your public key. The network verifies the transaction and records it on the blockchain. In your wallet you see the received coins.
- Sending funds. To transfer money, you sign the transaction with your private key. The network verifies the signature, and the funds are sent to the recipient.
Important: a digital wallet is not a 'cryptocurrency storage' but a means to interact with the blockchain. Coins always remain on the network.
How custodial wallets work
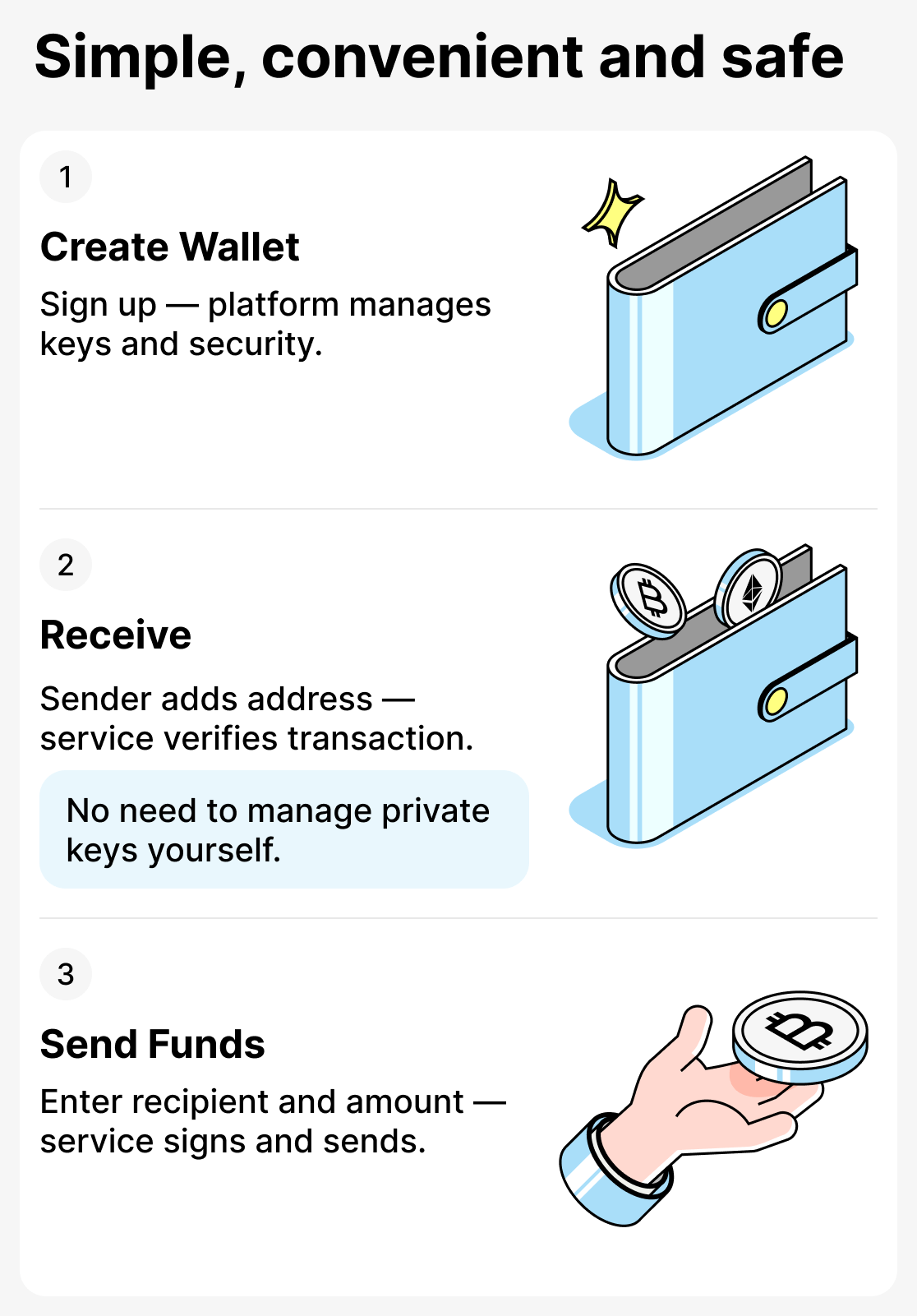
The principle of operation can be described as follows:
- Creating a wallet. The user registers with the service or application and creates an account. You receive a convenient interface for working with cryptocurrency without the need to manually generate private keys or a seed phrase.
- Receiving funds. The sender specifies your crypto wallet address. The service automatically verifies the transaction and displays the incoming coins in your wallet. The user does not need to interact directly with the blockchain.
- Sending funds. To transfer cryptocurrency, you simply enter the recipient's wallet address and the amount in the app. The service signs the transaction on your behalf, verifies it and sends the funds. Everything happens quickly, securely and without unnecessary technical complexity.
Unlike non-custodial wallets, where the user manages the private keys and bears full responsibility for security, custodial wallets remove this burden. All operations — from creating a wallet, receiving funds, and sending cryptocurrency — are carried out in a convenient app, and access keys are securely stored by the service. This makes working with cryptocurrency simple, fast, and secure.
How to choose a crypto wallet for your needs
If you need full control, aren't afraid of complexity, and are even a bit paranoid about security — a non-custodial wallet is right for you. It's an option for those who like to do everything themselves: storing keys and handling technical issues. With a non-custodial wallet, you are the bank, the security service, and the technical specialist all in one. If you prefer complete independence, a non-custodial wallet is your choice.
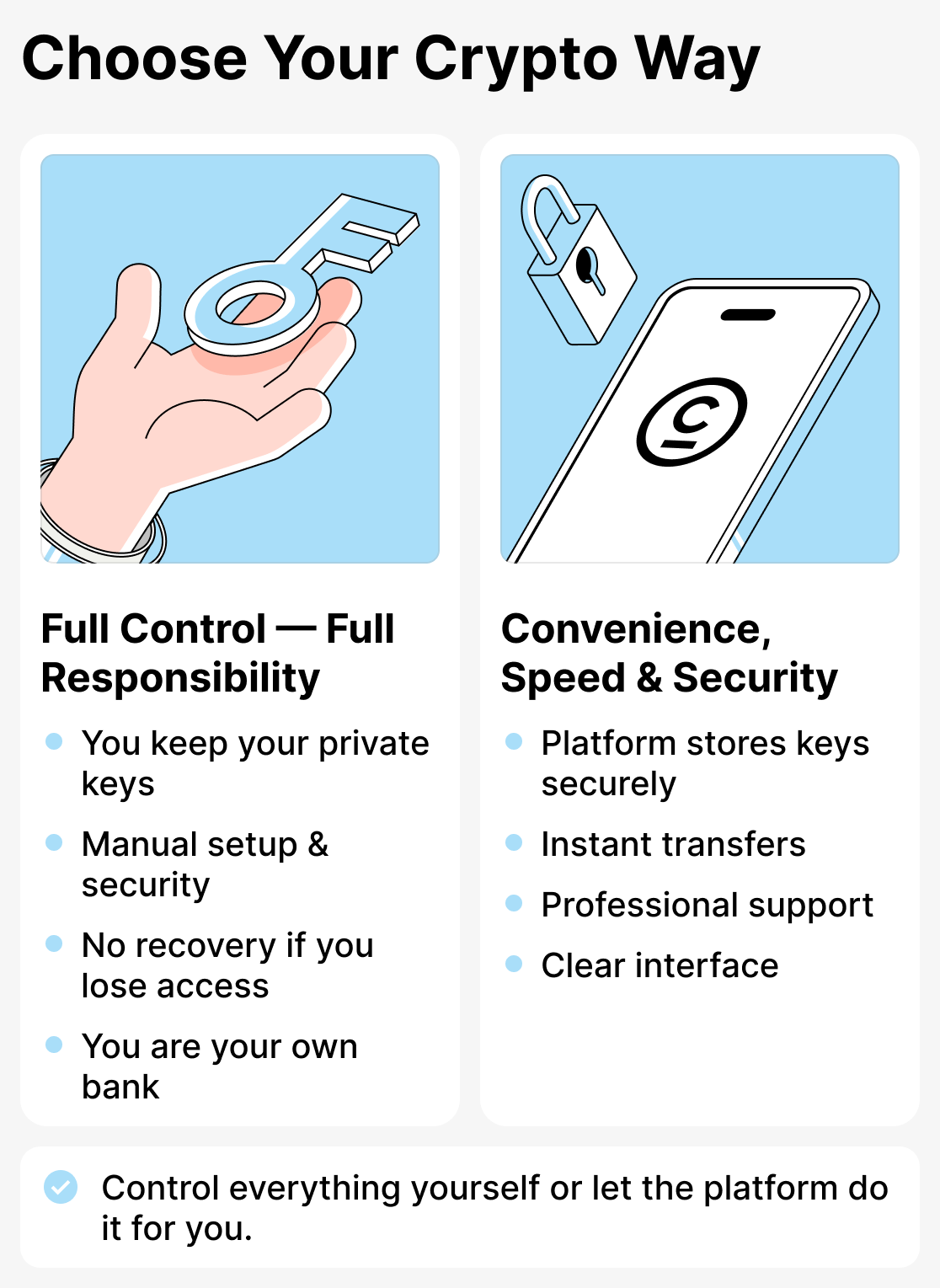
If you want everything to be convenient, fast and secure without unnecessary complications — choose a custodial wallet. As professionals, we recommend this option. The process is similar to a traditional bank: the service is responsible for security, transfers are instant, the interface is intuitive, and support is always available.
We have a detailed article on how to set up a crypto wallet. Read it to clarify the details and be able to set everything up right away!
How Cropty Wallet simplifies working with cryptocurrency
It doesn't matter whether you're new to cryptocurrency or already an experienced blockchain user, Cropty Wallet is ideal for both beginners and professionals. This custodial hot wallet combines convenience, security, and functionality, which definitely sets it apart from similar solutions.
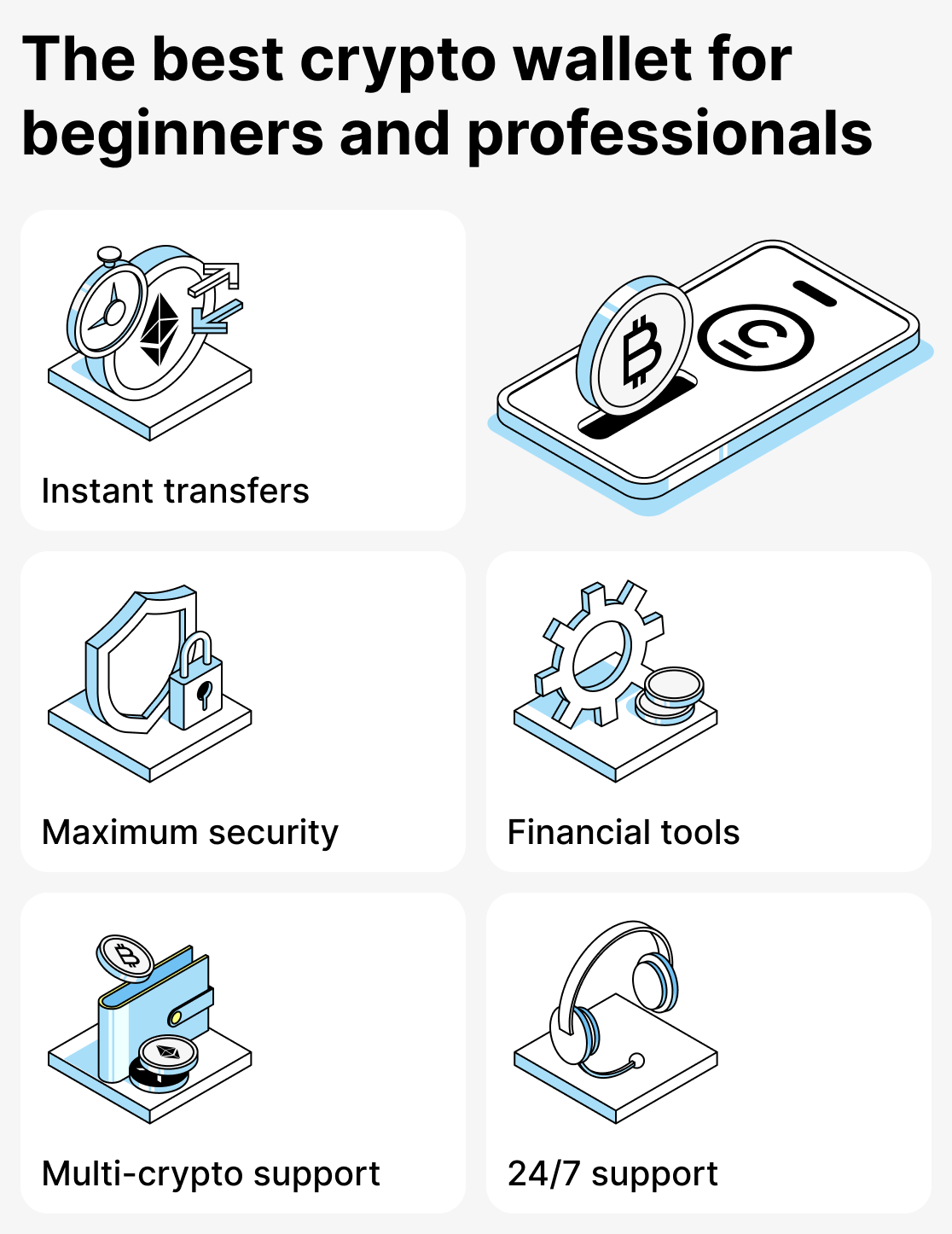
With Cropty Wallet you get:
- Instant transfers without unnecessary fuss;
- Support for multiple cryptocurrencies in a single app;
- Built-in financial features — crypto lending, staking, external transfers and internal transfers between users without commission;
- Professional 24/7 support that responds in the user's language;
- Maximum protection of funds — the platform itself is responsible for safeguarding the private keys. In the event of key theft or an unforeseen error, the service will do everything possible to rectify the situation.
Cropty Wallet is a blockchain wallet that truly makes users' lives easier, providing security, simplicity, convenience, and full control over finances. Forget about complicated procedures, losing private keys, and the need to spend time learning a complex interface!
Cropty Wallet – your friend and assistant in the world of cryptocurrencies!
Frequently asked questions about crypto wallets
What is a crypto wallet in simple terms?
A crypto wallet is a tool for storing and managing cryptocurrency. Funds are not actually stored in it, since the coins always reside on the blockchain itself. With a crypto wallet, you can access and use coins via a private and public key, or send them to other users.
What is the difference between a hot wallet and a cold wallet?
A hot wallet is constantly connected to the internet. It is convenient for everyday use: frequent transfers.. A cold wallet is not connected to the internet. It is a physical storage device that provides maximum security for assets. Such a wallet is ideal for long-term storage of large sums.
Which to choose: custodial or non-custodial wallet?
It all depends on your priorities, experience, and preferences. If you value comfort, security, and convenience, consider custodial wallets — these platforms store private keys and assume responsibility, and they also provide customer support. If you are an experienced user who wants full control and understands the risks, you can choose a non-custodial digital wallet; in that case you are responsible for security, and transactions are executed strictly according to the protocol.
What to do if you lost your seed phrase?
If you used a non-custodial wallet, it will be impossible to restore access if you lose your seed phrase. If, however, you stored your assets in a custodial wallet (for example, Cropty Wallet), simply use the account recovery feature or contact support.
Which crypto wallet is best for a beginner?
Newcomers should choose custodial wallets, as they are convenient — the platform takes responsibility for mistakes and glitches, and the service's support will always help resolve the user's problem.
Can different cryptocurrencies be stored in one wallet?
Yes, many modern multi-currency wallets (including Cropty Wallet) support dozens of cryptocurrencies and allow you to manage them in a single app.