Crypto lending has become one of the key areas of development in digital finance these days. Any user can now take a loan secured by cryptocurrency and obtain liquidity without selling their assets. Numerous centralized and decentralized platforms issue such loans, offering a wide range of terms. However, all crypto lending models have one thing in common: the need for collateral. This is because the cryptocurrency market is extremely volatile, meaning the value of coins is constantly changing. To protect themselves against non-repayment and the loan losing value, platforms impose this requirement.
That said, the world of cryptocurrencies doesn't stand still and is constantly evolving. Alongside the traditional lending model, flash loans have emerged fairly recently.
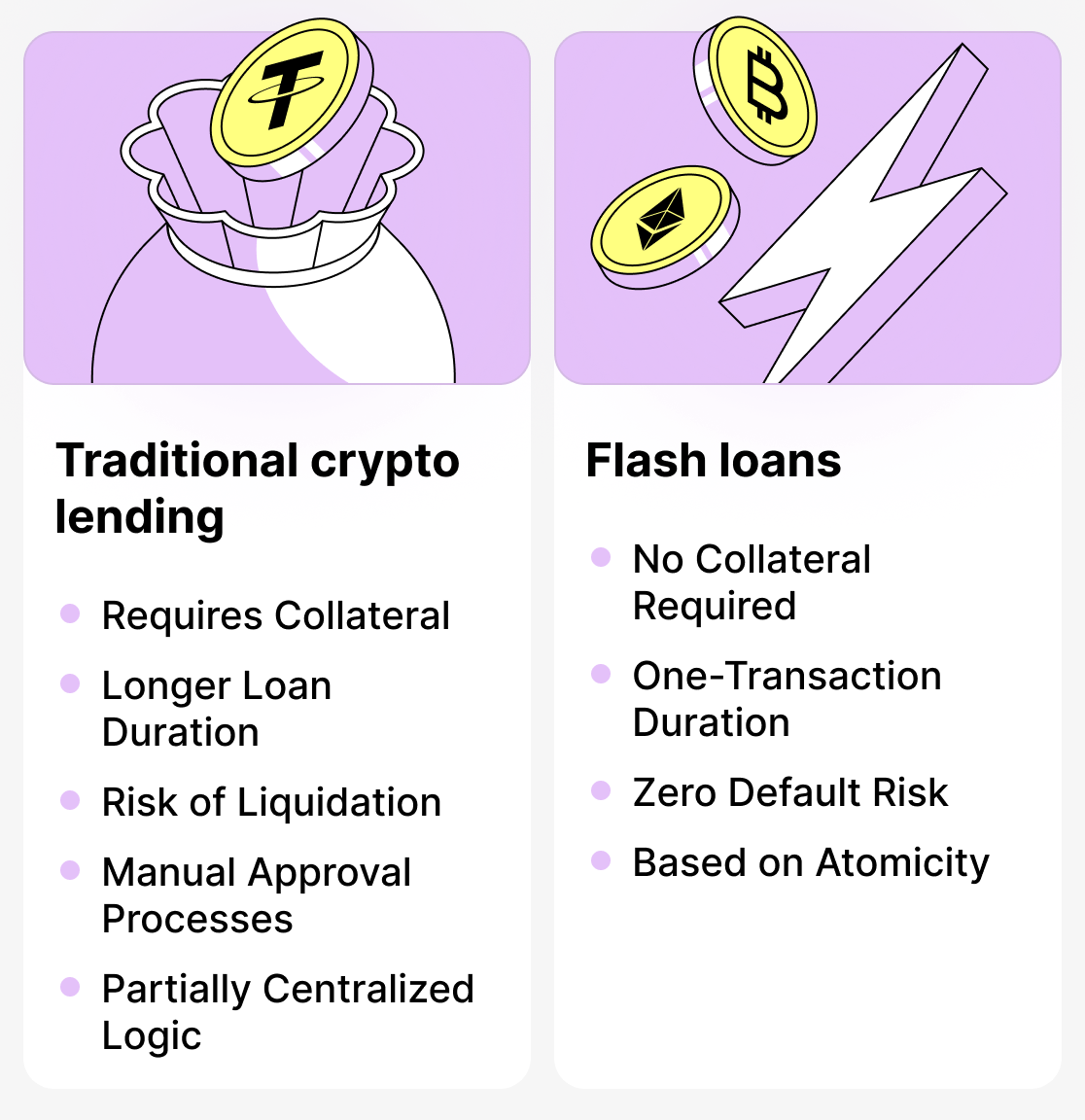
Flash loans are unusual loans that completely break the logic of crypto lending. Such loans are issued to the borrower instantly and without collateral for exactly one transaction! If the repayment conditions are not met, the operation is simply reverted. This way the platform does not incur any losses.
How flash loans work in simple terms
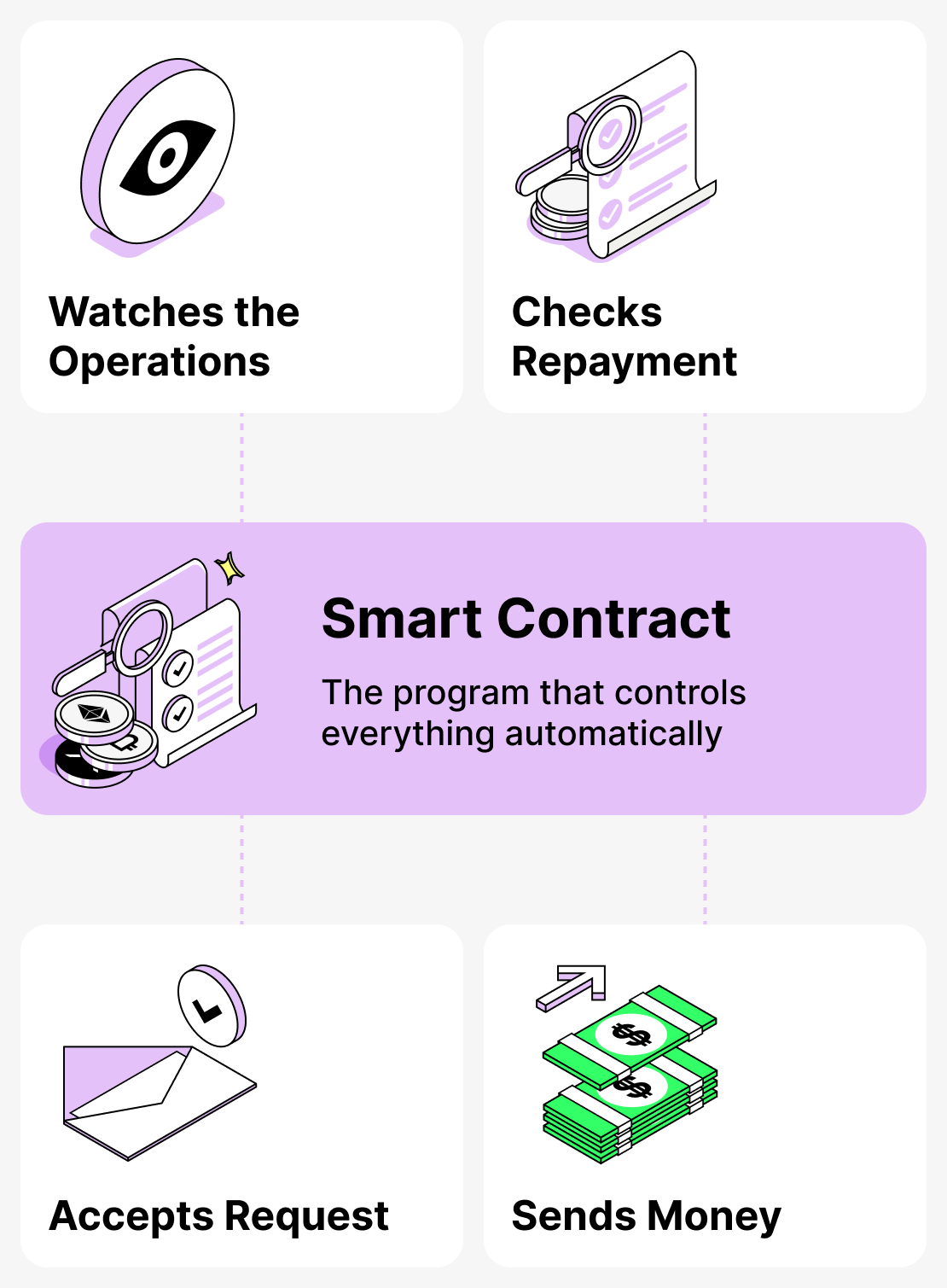
Flash loans — they are not something magical. They are possible thanks to the features of the blockchain itself, namely the operating principle of smart contracts (program code): the atomicity of transactions.
What is transaction atomicity
Any transaction on the blockchain consists of a set of operations. They are executed sequentially, and a successful result is recorded only if all operations have been completed. If at least one condition is violated — the transaction is cancelled. It is this property of the blockchain that is called atomicity. Flash loans rely on it.
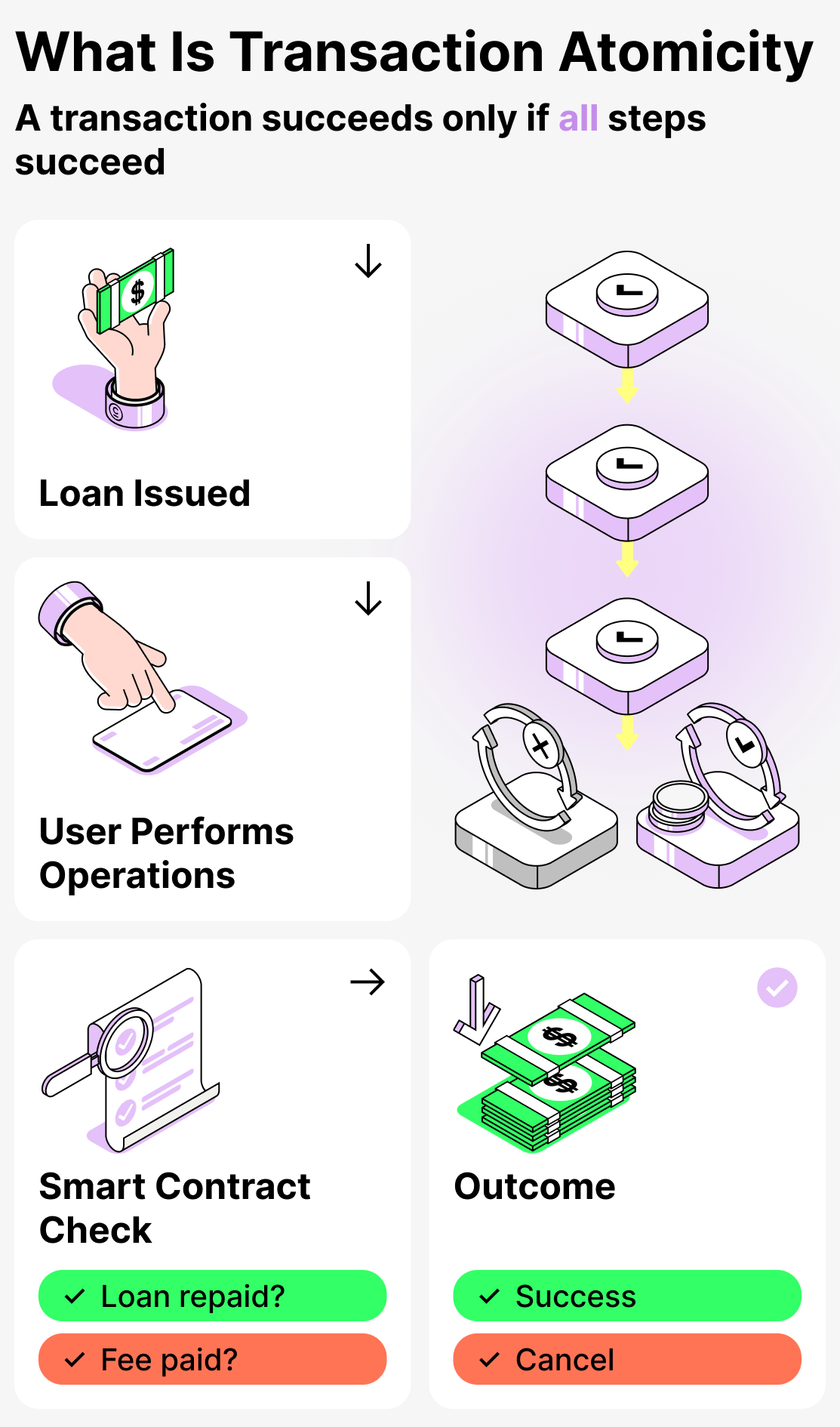
How it works:
- The platform extends credit to the user;
- The user conducts the required operations using these funds (participates in arbitrage trading, etc.);
- When the transactions are completed, the smart contract checks whether the borrower has repaid the loan and paid the fee.
If all conditions are met — the transaction is considered valid and is recorded in a block. But if not — it is canceled. It turns out as if nobody ever issued the money.
Thus, the platform issuing the loan will not incur losses, because it is technically impossible for the loan not to be repaid.
The role of smart contracts in issuing flash loans
Flash credit — a fully automated feature. It is issued only when all conditions originally defined by the platform are met.
Here's an example of a standard algorithm for issuing a flash loan:
- The borrower requests a flash loan and has received the funds;
- The user performs a series of transactions using borrowed funds;
- After all transactions have been completed, the loan must be repaid with the fee taken into account;
- If all conditions are met, the transaction is approved and recorded on the blockchain.
A smart contract (program code) acts as the guarantor of such a transaction. No intermediaries take part in flash lending: customer support, managers, or others.
How to take a flash loan: a step-by-step guide
To understand how flash loans work, it's important to see the whole process from start to finish. It may all seem complicated, but at its core a flash loan is simply a strict sequence of actions within a single transaction.
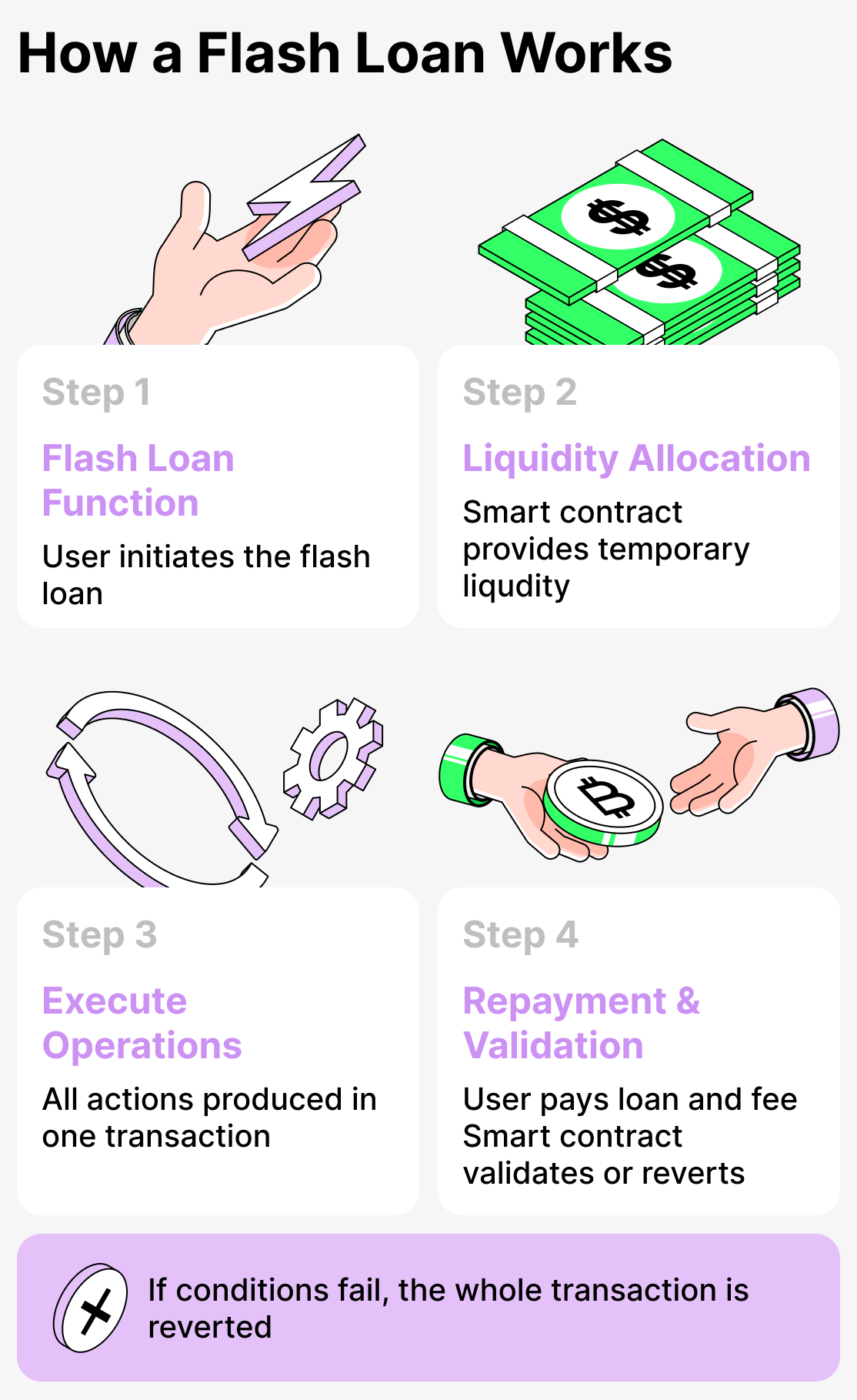
Below is a step-by-step guide on how to take a flash loan:
Step 1. Choose the flash loan function
On most platforms, this feature is offered either on the main screen or in the “Lending” subsection. It is usually called:
- flashLoan;
- flashBorrow;
- flashSwap
The user finds this feature and selects it, then accepts all terms. At this stage, essentially nothing happens yet: the platform simply receives the user's command.
Step 2. Release of funds
The lending protocol's smart contract temporarily allocates assets from the liquidity pool to the user.
The following assets are most commonly issued:
- ETH,
- USDT/USDC,
- BTC
The loan amount can be enormous. Sometimes a user can receive cryptocurrency worth several million dollars. It all depends on how much funding the user needs and whether the platform can provide it.
Step 3. Executing the action chain
After the loan is approved, a transaction is created in which the user can perform one or more operations:
- Participate in arbitrage trading;
- Replace your collateral in the lending protocol;
- Refinance position;
- Liquidate someone else's debt;
- Create a complex financial chain (for example, leveraged yield farming).
All operations involving borrowed funds are executed only within a single transaction!
Step 4. Repayment of the loan amount and payment of the fee
After the borrower has completed all operations with the borrowed funds, they must repay the loan and pay the fee. Only then will the transaction be counted! The smart contract automatically verifies:
- Was the debt paid in full,
- Has the borrower paid the fee? Usually it is small (often fixed).
If everything is done — the transaction is executed.
What will happen if you don't repay the debt and don't pay the fee
If the user has not fulfilled their obligations to the platform, the smart contract will cancel the transaction. In other words, it is simply "not executed". This way the platform loses nothing, and the user receives nothing.
Overview of the flash loan process
Such a loan can be described as "receiving funds for a single transaction only". If all conditions are met: both the borrower and the platform come out "ahead". But if not — no one loses anything.
Why flash loans are needed: real use cases
Flash loans are gaining widespread popularity because they enable actions that are impossible or require enormous capital in conventional crypto lending. They are not used to get money for "everyday expenses" but rather for specific purposes.
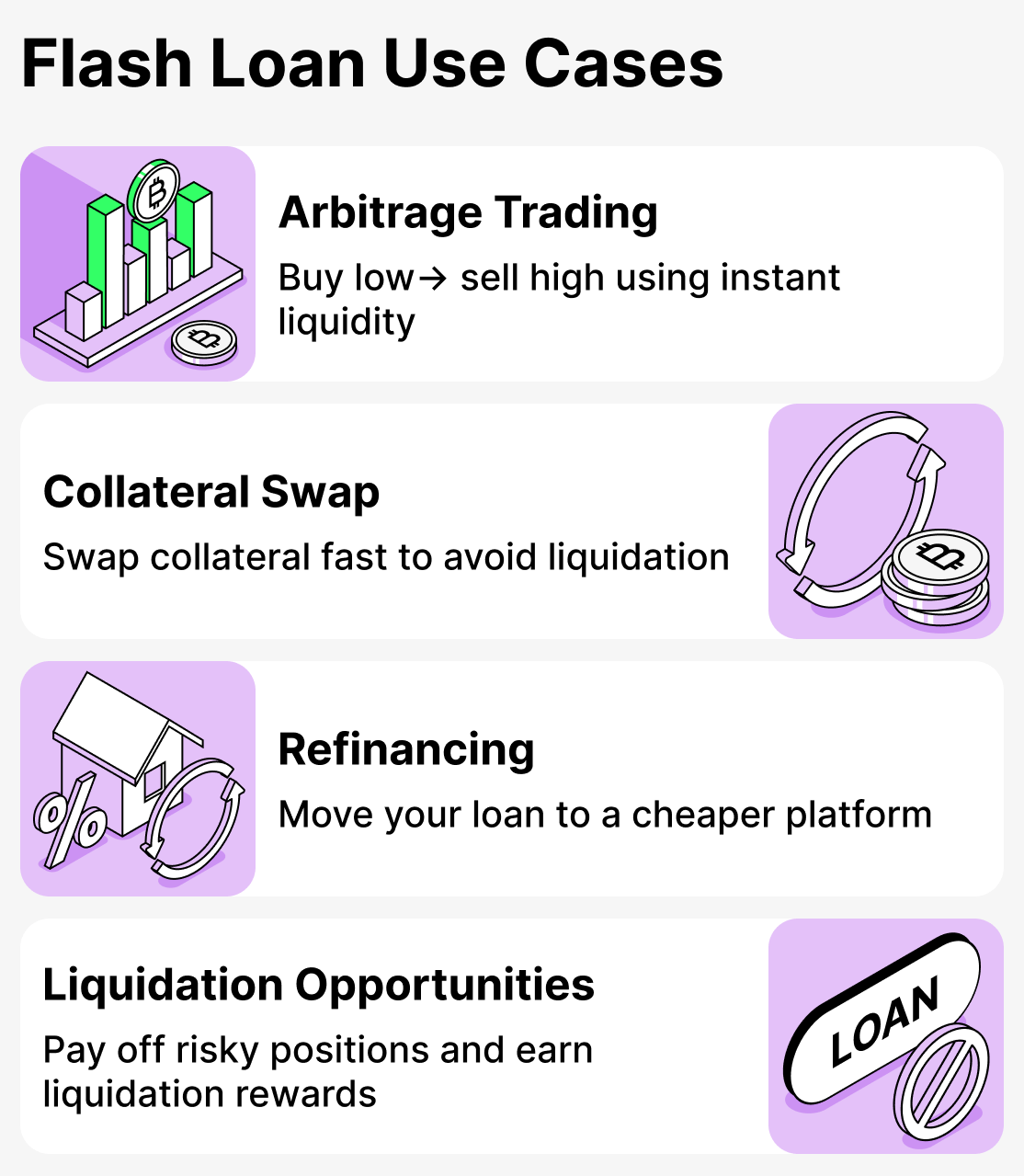
Let's look at the most common and straightforward use cases for flash loans:
Arbitrage trading
This is exactly where such loans are used most often! Different decentralized exchanges can show different prices for the same token for several seconds or minutes.
A user participating in arbitrage trading takes a flash loan, buys a token on an exchange offering a lower price, and sells it on an exchange where the asset is priced higher. After that, the borrower repays the loan and realizes a profit from the difference.
Why it's relevant:
- With a flash loan, you don't need to use your capital or spend time transferring funds.
- A single successful trade of this type can yield a substantial profit.
Collateral swap
Sometimes an asset used as collateral for a loan can suddenly lose value. You don't always have the option to immediately repay part of the debt or top up the collateral with available funds. But you must act quickly, or you could lose your assets! That's where a flash loan can help.
Suppose a user has an active loan collateralized by ETH. But suddenly the price of ETH starts to fall. To prevent liquidation, the user can replace the collateral with a more stable asset (for example, USDT). To do this, they take a flash loan, close the active position, open a new one with different collateral, and then repay the loan.
Refinance Position
This is similar to a collateral replacement scenario; however, in this case the borrower's goal is to take out a loan on more favorable terms.
For example, a user has an active loan at 9% annual interest. But at some point they find a platform that offers the same loan on better terms, say at 5% annual interest. So the borrower takes a flash loan, closes the active position, and opens a new, more favorable one. And all of this happens within a single transaction!
Participation in debt liquidations
In the world of cryptocurrencies there is a special caste of people called "liquidators". These users receive rewards for repaying other users' loans. Thus, with the help of flash loans you can earn a decent profit if you understand the process.
How it works (briefly):
- The user finds a 'problematic' position of a certain borrower;
- Takes a flash loan;
- Repays someone else's debt with borrowed funds;
- Receives payment for debt liquidation;
- Returns the loan.
With a flash loan, you can react quickly and, as a result, earn some extra profit!
Where are flash loans used
Flash loans — a way to execute complex financial operations in a short time without the need to use your own funds. They are used for various purposes, for example in trading or in traditional crypto lending. And most interestingly — such loans can help you profit where a quick reaction is required.
Advantages of flash loans in DeFi
Flash loans are often associated with complex, opaque operations available only to the "chosen few". However, their applications are far broader than they may appear at first glance, and the opportunities they open up for users truly deserve attention.
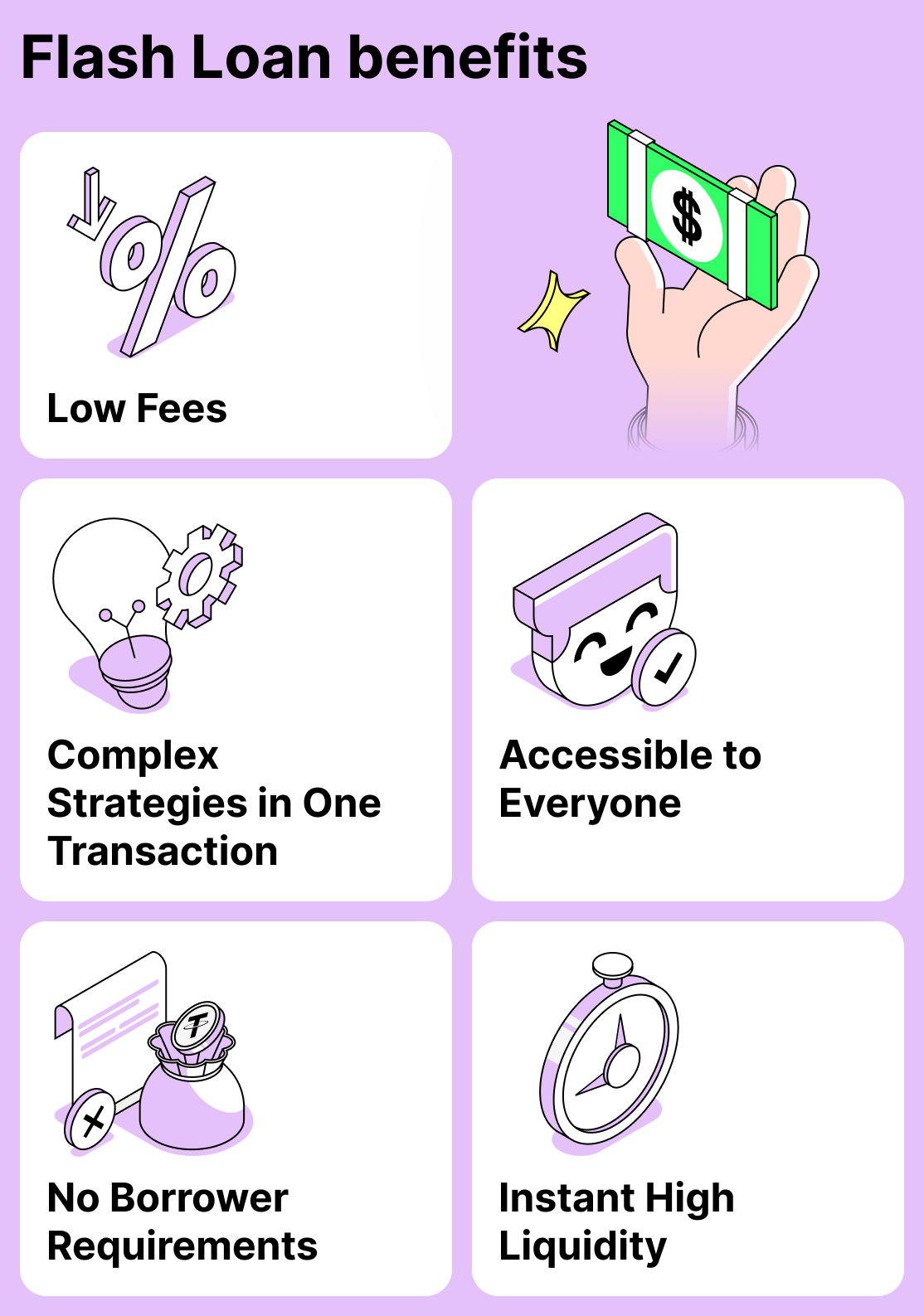
Here are several key advantages that have made flash loans resonate with a wide audience:
There are no requirements for the borrower.
Traditional crypto loans require borrowers to secure the loan with collateral, and the risk of position liquidation is always present. Flash loans, on the other hand, allow anyone to obtain funds within a very short timeframe. They can be taken by any user who knows how to interact with smart contracts.
Quick access to a large amount of funds
Flash loans allow you to borrow an amount that can exceed a user's entire capital many times over. Need a million? No problem! (only if it's available in the pool). The main condition is that the user must repay the entire amount within a single transaction and also pay a fee.
Ability to build a chain of complex operations
Traditional lending is limited to a number of simple scenarios. Typically, you can take out a loan, use the funds to buy tokens, spend them, and repay the loan later. Flash loans open the door to complex strategies.
This way, the user can, for example:
- Engage in arbitrage trading between multiple exchanges;
- Transfer collateral between protocols;
- Set up automatic loan refinancing;
- Set up multi-level schemes to generate additional income (for example, participating in collateral liquidations for a reward).
What used to require enormous capital and dozens of consecutive transactions now fits into a single transaction.
Wide availability
In traditional finance, complex operations are accessible only to major players. Flash loans enable ordinary users to access the same mechanisms professionals use. If you have the funds, flash loans open every door.
Low fees (relative to the transaction amount)
Most protocols charge a tiny percentage for facilitating a flash loan. For example, a fee of 0.09% of the transaction amount is common — this is especially relevant for large transactions.
Flash loan risks and common hacker attacks
Although flash loans are technically safe for protocols (a borrower's failure to repay is impossible), they have become a popular tool in the hands of hackers. The reason is simple: a flash loan allows one to obtain a huge sum of funds instantly and without collateral. This enables malicious actors to reap large profits and inflict significant damage on both the protocol and its users.
Here are the main types of attacks that appear in most cases:
Price and oracle manipulation
This is the most common type of flash loan attack. The attacker takes a large loan and uses it to change the asset price in a DEX pool (shift the pool balance). A protocol that uses the DEX’s internal prices as an oracle incorrectly treats the new price as valid. The hacker withdraws assets or takes an inflated loan, then simply repays the flash loan and pockets the profit.
The problem here is no longer with the flash loans themselves, but with the protocols that use reliable oracles to determine prices.
Attacks on smart contracts through logical errors
Flash loans allow executing a large number of operations within a single transaction, making them an ideal tool for attacking vulnerable asset price calculation methods and balance display functions. If a platform does not take into account or monitor extreme price changes, a flash loan can artificially create conditions that lead to an error.
Sophisticated combined attacks
Although classic hacks have become rarer, the emergence of flash loans has provided attackers with new methods to profit from unreliable platforms. For example, a hacker can take out a flash loan, carry out a series of attacks with it on several protocol elements, close the position, and repay the loan. Using flash loans, attackers can create an entire "chain" of fictitious operations.
Using low fees to carry out multiple attacks
Sometimes protocols set very low fees for taking out flash loans. This allows attackers to repeat the attack multiple times!
Flash loans today: advantages, risks, applications
Today flash loans are not just some new "opportunity for the chosen few." They are a full-fledged financial instrument used by both professionals and those with "intermediate" knowledge. This type of lending lets you obtain funds without collateral here and now for a specific purpose, which is especially relevant for those who use cryptocurrency to generate income.
That being said, it should be noted that flash loans are not suitable for everyone. If you are new to the world of cryptocurrencies, it's better to begin with traditional crypto lending. We have a detailed article on how crypto lending works and how to take out a crypto loan in a few simple steps. Read it to clarify all the details!